Efficiently Driving Protein-based NMR Fragment Screening and Lead Discovery
Dr. Andrew “Dru” Namanja, Principal Research Scientist at AbbVie, will explore the potency ranking methods involving both qualitative single-point ligand concentration (Q Score) and quantitative binding affinity (KD), and how the combined utility can be used successfully to drive a Fragment-Based Drug Discovery (FBDD) campaign.
SPEAKER
Dr. Andrew “Dru” Namanja (AbbVie)
Abstract
Intro
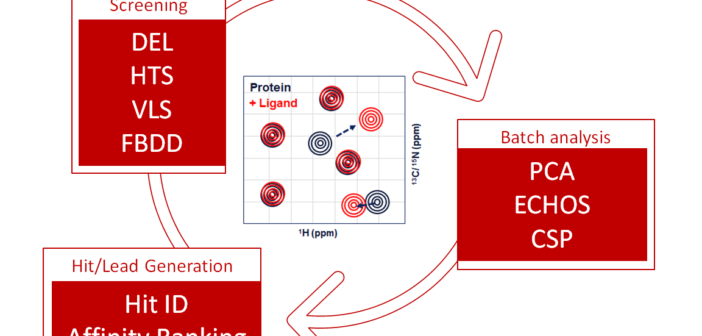
Protein-based nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an established gold-standard biophysical tool in early-stage drug discovery that provides atomic-resolution insights into protein-ligand interactions in solution. It ensures accurate confirmation of screening hits and drug leads by reducing the number of false positives and thereby saving resources and time in fast-paced setting with a high target attrition rate
Overview
The various applications of protein-based NMR in early-stage drug Discovery will be discussed, including classifying ligand mode-of-action (MoA), hit identification and confirmation from typical small molecule screening modalities such as DNA-encoded libraries (DEL), high-throughput screening (HTS), virtual library screening (VLS), and fragment-based screening (FBS).